Student Name(s): Grade:
Physical Geology 101 Laboratory
Topographic Maps and Orienteering Lab
Introduction & Purpose:
Topographic maps are much scaled down
two-dimensional paper models of the Earth’s three-dimensional land
surface. The characteristic that makes
topographic maps unique are contour lines, which are map symbols that express
surface relief – ground elevation changes across a given tract of land. Each contour line represents a continuous set
of surface point locations that have equal elevation. The topographic (“topo”
for short) map is an ingenious invention that helps humans navigate across the
Earth’s surface, and analyze the Earth’s surface morphology, and geology.
Learning how to read and create topographic
maps can be difficult, especially for those people who are not graphically
and/or three-dimensionally minded.
However, if the basic concepts of contour lines, map scale, and
coordinate positioning systems are properly understood, then
the ability to both read and create topographic maps will come much easier. The
purpose of this lab is to learn how to read, interpret, utilize, and create
topographic maps and topographic map profiles.
The major objectives of this laboratory
exercise are as follows:
1) Be able to interpret all the necessary map
information, including map scale, declination, contour interval, map symbols,
and map coordinates.
2) Be able to locate and identify features on a map,
including the use of map coordinates, identifying geographic features, and
reading and assigning compass bearings.
3) Be able to construct a simple topographic profile.
4) Be able to use a compass for orienteering purposes.
Part I.
Instructions: Carefully read and analyze the section 9A in your
lab manual – pages 168
through 184.
Then complete the following exercises on page 185 and 186 in your lab.
manual. Complete your answers below using the
corresponding Figures.
Section 9A Questions and Answer Sheet
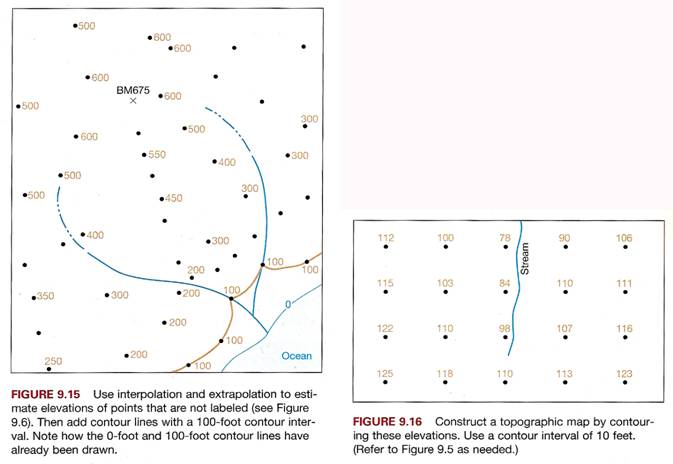
1. Draw contour lines with 100-foot intervals on
Figure 9.15. Refer to Figure 9.6 if
needed.
2. Draw contour lines with 10-foot intervals on
Figure 9.16. Refer to Figure 9.6 if
needed.
3. Color/shade in the area that represents the
top of the highest hill on the map in Fig. 9.17
4. Place correct contour value in empty box on
map in Figure 9.18. Then color/shade in
area that
represents the lowest elevation on the map.
Finally, label a “closed depression”
with the
initials “CD”.
5.
Complete the topographic map in Figure 9.19 using a contour interval of 10
feet. Make
sure to label
each contour line with its exact elevation above sea level.
6. Refer to map in Figure 9.20 -
a) contour interval = ___meters b)
total relief = ____ meters
c) Slope
gradient from “X” to “Y”? =
______ meters per km d)
Draw road from “A” to “B”
Work Sheet for Part II. -
Questions #1 through #6


Part II. Analysis of the Yosemite Valley Topographic Map
Instructions: Complete the following map analysis activities for
the Yosemite Topographic Map
supplied by
your instructor.
Section A: Topographic
Fundamentals and Features
7. What year was this map
published? _________
8. What organization created this
map?
______________________________________
9.
How was topographic contouring of this map generated? _______________________
10. What type of map projection was used to create this
map? ________________________
Coordinate Systems
11. What are the longitude and latitude for each
of the two opposite corners of this map?
NW Corner SE Corner
Longitude: ______________ ______________
Latitude: ______________ _____________
12. What are the longitude and
latitude tick mark intervals along the edge of the map? ______
13. Which UTM zone does this map
area located in? ______
14. What color are the UTM coordinate tick marks found
along the outside edge of this map?
Answer: _________________
15. What are the UTM coordinates for each of the
two opposite corners of this map?
NW Corner SE
Corner
Easting: ______________ ______________
Northing: ______________ ______________
16. What are the blue UTM tick mark
intervals along the edge of the map?
____ meters apart
Map Scale
17. What is the ratio scale of this map? _______________
18. What is the verbal scale of map? One inch of map distance equals ______ inches of
real
ground distance.
19. Roughly how many square miles of real ground does
this map cover? ______________
Magnetic Declination
20. What is the magnetic declination? ___________ (Make sure to note East or West)
21. Name the topographic map that continues to the NE of
this map? _________________
Map Features and Symbols
22. What is the difference between the
solid green pattern and small dotted green pattern on
this map?
_______________________________________________________________
23. Difference between the black dashed single lines and
the black dashed double lines?
__________________________________________________________
24. Difference between the black dashed and solid double lines ?_____________________
25. What
type of symbols represents buildings on the map? ________________________
Section B: Location, Bearing, and Distance
Establishing
Location
26. Interpolate
the best approximate longitude and latitude for these locations:
Half Dome
Longitude: _______________________ ________________________
Latitude: _______________________ _________________________
27. Interpolate the best approximate longitude and latitude for these
locations:
Clouds Rest Mt Star King
Easting: _______________________ ________________________
Northing: _______________________ _________________________
Establishing Bearing and Distance
28. Calculate
the bearing and distance from Half Dome to Clouds Rest.
Quadrant bearing: _________________
Azimuth bearing: _________________
Distance (miles): _________________
29.
Calculate the bearing and distance from Glacier Point to
Quadrant bearing: _________________
Azimuth
bearing: _________________
Distance (miles): ________________
Section C: Contours and Surface Relief
Contours
30. What is the contour interval of the map? ______________
31. What is the contour interval between the
dark/thicker contour lines?
_____________
32. What is the base level datum (“zero” elevation used
to establish all contour and point elevations on this map? ___________________________________
33.
What is the highest measured elevation (benchmark) on this map?
________________
34.
What is the lowest measured elevation (benchmark) on this map?
_________________
35.
What is the total relief of this area?
__________________
Contours Patterns
36. Very
tightly-spaced contour lines represent what type of geographic features?
Answer:___________________________
37. Very
broadly-spaced contour lines represent what type of geographic features?
Answer:___________________________
38. Sets
of contour lines that form “V”-shaped patterns pointing to lower elevations
represent what sort of general geographic feature? (hint:
either stream channels or ridge lines)
Answer:___________________________
39. Sets of contour lines that form “V”-shaped patterns
that point to higher elevations
represent what sort of geographic feature? (hint: either valley bottom or ridge
line)
Answer:___________________________
Geographic Features
40. Which
direction does the Merced River Flow through
Answer:
_________________________________________________________________
41. What
special name is used in
Section D: Topographic Profiles
of Yosemite Valley
Directions: Follow the steps on
page 187 to create a topographic profile (see Figure 9.22). Note
that the vertical exaggeration of a topographic profile is
defined as the difference between the
vertical
(elevation) scale and the horizontal (lateral ground distance) scale.
42. Construction of the Tanaya Creek Profile A-A’
Instructions: Construct a topographic profile of the eastern end of
Tanaya Creek
from the top of Mt. Watkins (A) to the top of Clouds Rest (A’).
a. Review
the instructions for creating profiles in your lab manual (Part 9B 0pg. 189)
b. Use only the dark/bold contour lines
c. Do not vertically exaggerate (your vertical scale is
the same as your horizontal)
43. Construction of the
Instructions: Construct a
topographic profile of the central portion of
The
Rocks (B’). Review points a-b-c above used for Tanaya Creek profile.
Comparison between the Tanaya Creek and the
44.
Describe the general shape of each of the profiles across
Tanaya
Creek Profile A-A’ - ___________
45. Compare
the two profiles described above in terms of “V” shaped versus “U” shaped.
Explain which type of erosional agent you think is
primarily responsible for the shaping of each of these two sections of
________________________________________________________________________
Part III. - Post Lab Exercise:
Laboratory Reflection
Write a short reflection (about a paragraph
length) about your experience in doing the plate tectonic and earthquake
exercises lab today. Include what you
learned from this laboratory; what was interesting; the problems and challenges
you encountered; and how this lab was designed (the good and/or bad).